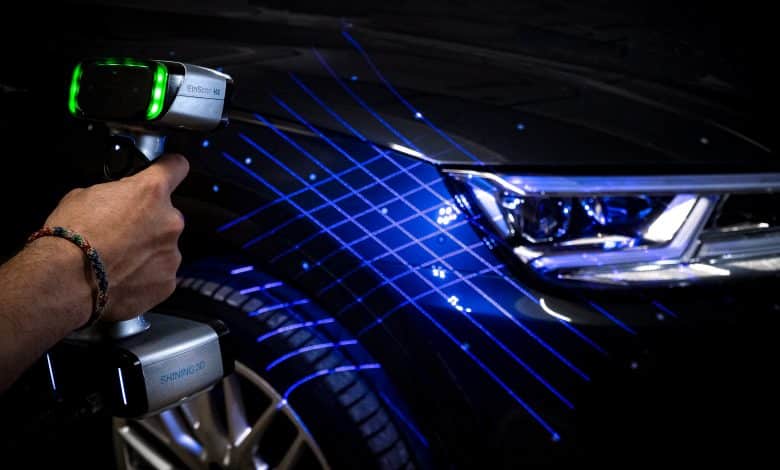
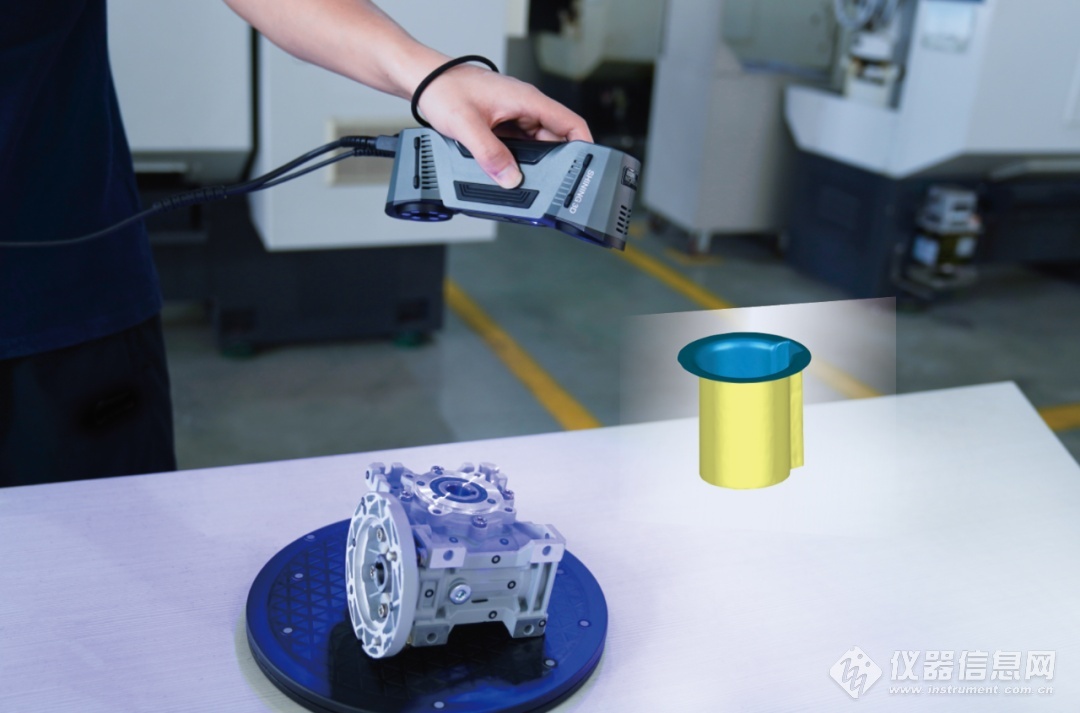
In the fast-evolving world of digital technology, 3D scanners have emerged as pivotal tools, transforming the way we capture and replicate the complexities of physical objects. These advanced devices play a crucial role in various industries, bridging the gap between the physical and digital realms.
Overview of Different Scanner Types and Their Uses
3D scanners come in various forms, each suited to different applications. Common types include:
- Handheld 3D Scanners: Known for their portability and versatility, scanners such as the Shining3D Einscan Pro 2X 2020 Scanner are ideal for capturing details of objects of varying sizes.
- Stationary 3D Scanners: Offering high precision, these scanners, which include the EinScan-SE (Elite) Desktop 3D Scanner, are used for industrial applications where accuracy is paramount.
- Structured Light Scanners: Scanners such as the Shining3D EinStar Handheld 3D Scanner utilise patterned light to capture detailed 3D images, perfect for intricate objects.
- Laser 3D Scanners: Employ laser technology to scan objects, widely used in sectors like manufacturing and engineering.
- Photogrammetry: This method uses photographs from different angles to create a 3D model, suitable for large-scale projects like mapping.
Key Factors in Selecting a 3D Scanner
 When it comes to selecting the ideal 3D scanner, it’s important to consider a range of factors that ensure you find a model best suited to your needs. The accuracy and resolution of a scanner are crucial in determining the level of detail and precision it can capture, which is vital depending on your application.
When it comes to selecting the ideal 3D scanner, it’s important to consider a range of factors that ensure you find a model best suited to your needs. The accuracy and resolution of a scanner are crucial in determining the level of detail and precision it can capture, which is vital depending on your application.
Equally important is the size and portability of the scanner, especially if you intend to scan objects in various environments or of different sizes. The compatibility of the scanner’s software with your existing workflow can’t be overlooked as it affects the ease of integration and efficiency. Lastly, your budget will play a significant role in your decision, as it’s essential to find a balance between the features you need and what you can afford.
How 3D Scanners Transform Various Industries
The impact of 3D scanners is evident across multiple industries, revolutionising traditional processes and introducing new possibilities. In manufacturing, these scanners are instrumental in quality control and reverse engineering, enabling precise replication and improvement of parts.
The healthcare sector benefits immensely, with 3D scanners aiding in the creation of custom-fit prosthetics and orthodontic devices. In architecture and construction, they offer the ability to model buildings and historical sites with unprecedented accuracy. The entertainment industry, too, has seen a transformation, with 3D scanners enhancing special effects and virtual reality experiences.
In conclusion, the indispensable role of 3D scanners in today’s digital landscape is clear. They offer unmatched efficiency and precision, significantly influencing various fields. As technology continues to advance, the scope and applications of 3D scanners are expected to expand, solidifying their status as essential tools in the modern digital workflow.